Skin Cancer Awareness: A Guide to Detecting and Preventing Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is one of the most common types of cancer worldwide, but it is also one of the most preventable. This blog aims to raise awareness about skin cancer, its causes, how to detect it early, and the necessary steps for prevention and care.
What is Skin Cancer?
Skin cancer occurs when the skin cells grow uncontrollably and form tumors. It can develop in any part of the skin, but the most common areas include the face, neck, arms, and legs. The three main types of skin cancer are:
- Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC): The most common and least dangerous form of skin cancer. It typically grows slowly and rarely spreads to other parts of the body.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC): This type can spread to other parts of the body but is usually treatable when detected early.
- Activation: Plasma is enriched with bioactive compounds.
- Melanoma: The deadliest form of skin cancer. It begins in the cells that produce pigment (melanocytes) and can spread rapidly to other organs if not caught early.
Causes of Skin Cancer
The primary cause of skin cancer is overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or artificial sources, such as tanning beds. UV radiation damages the DNA in skin cells, leading to mutations that can result in cancer. Several factors contribute to the risk of developing skin cancer, including:
- Excessive sun exposure: Long-term exposure to UV rays, particularly without protection, increases the risk of skin cancer.
- Tanning beds: The use of tanning beds, especially by young people, increases the risk of skin damage and cancer.
- Fair skin: People with lighter skin, freckles, and red or blonde hair are more prone to sunburns, which increases the risk of skin cancer.
- Family history: If someone in your family has had skin cancer, your risk may be higher.
- Weakened immune system: People with weakened immune systems, such as those undergoing chemotherapy, are at higher risk.
- Age: The risk of skin cancer increases with age, although younger people are also susceptible, particularly to melanoma.
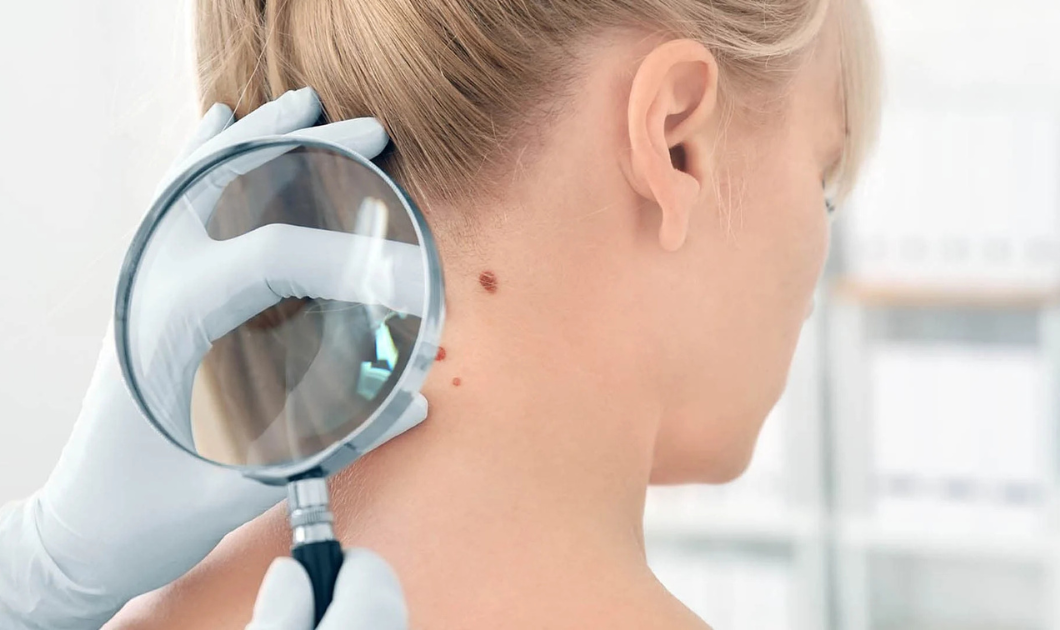
How to Detect Skin Cancer Early?
Early detection is crucial for successful treatment. Regular self-examinations and professional skin checks can help identify skin cancer before it spreads. Here’s how you can detect potential signs of skin cancer:
Regular Skin Checks: Inspect your skin for any changes in existing
moles, spots, or the appearance of new growths. Look for asymmetry, uneven borders, or
changes in color.
ABCDEF Rule: Use this simple guide to identify suspicious moles:
- A: Asymmetry – One half of the mole doesn’t match the other.
- B: Border – Irregular, scalloped, or poorly defined edges.
- C: Color – Multiple colors or uneven pigmentation.
- D: Diameter – Larger than 6mm, about the size of a pencil eraser.
- E: Evolving – Any change in size, shape, or color over time.
See a Dermatologist: If you notice any of these signs, make an appointment with a dermatologist for professional evaluation and possible biopsy.
Prevention and Proper Care
While it may not be possible to completely avoid skin cancer, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk:
- Use Sunscreen: Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher, even on cloudy days. Reapply every 2 hours or after swimming or sweating.
- Seek Shade: Stay out of direct sunlight, especially between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., when UV rays are the strongest.
- Wear Protective Clothing: Wear hats, sunglasses with UV protection, and long-sleeved clothing to shield your skin from UV exposure.
- Avoid Tanning Beds: Steer clear of tanning beds and other artificial UV sources, as they increase your risk of skin damage.
- Self-Examine Your Skin: Perform regular self-checks of your skin every month, looking for any unusual spots or changes in existing moles.
- Regular Dermatology Visits: Schedule annual skin exams with a dermatologist, especially if you have a family history of skin cancer or high sun exposure.
Skin cancer is preventable with awareness and care. Recognizing the signs, using sun protection, and doing regular checks can help reduce your risk.
Stay informed and take action to protect yourself and others. Always prioritize your skin’s health.